Evaluación de Curcumina Empaquetada en Ácido Poliláctico-Co-Glicólico (Nano-Cur-Plga) en el Modelo Experimental de Enfermedad de Alzheimer Inducido Caenorhabditis Elegans Gmc101
Evaluation of Curcumin Packaged in Polylactic-co-glycolic acid (NANO-CUR-PLGA) in the Experimental Model of Alzheimer’s disease induced by Caenorhabditis Elegans GMC101
Barra lateral del artículo

Términos de la licencia (VER)

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Declaración del copyright
Los autores ceden en exclusiva a la Universidad EIA, con facultad de cesión a terceros, todos los derechos de explotación que deriven de los trabajos que sean aceptados para su publicación en la Revista EIA, así como en cualquier producto derivados de la misma y, en particular, los de reproducción, distribución, comunicación pública (incluida la puesta a disposición interactiva) y transformación (incluidas la adaptación, la modificación y, en su caso, la traducción), para todas las modalidades de explotación (a título enunciativo y no limitativo: en formato papel, electrónico, on-line, soporte informático o audiovisual, así como en cualquier otro formato, incluso con finalidad promocional o publicitaria y/o para la realización de productos derivados), para un ámbito territorial mundial y para toda la duración legal de los derechos prevista en el vigente texto difundido de la Ley de Propiedad Intelectual. Esta cesión la realizarán los autores sin derecho a ningún tipo de remuneración o indemnización.
La autorización conferida a la Revista EIA estará vigente a partir de la fecha en que se incluye en el volumen y número respectivo en el Sistema Open Journal Systems de la Revista EIA, así como en las diferentes bases e índices de datos en que se encuentra indexada la publicación.
Todos los contenidos de la Revista EIA, están publicados bajo la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Licencia
![]()
Esta obra está bajo una Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-NoDerivativa 4.0 Internacional
Contenido principal del artículo
Resumen
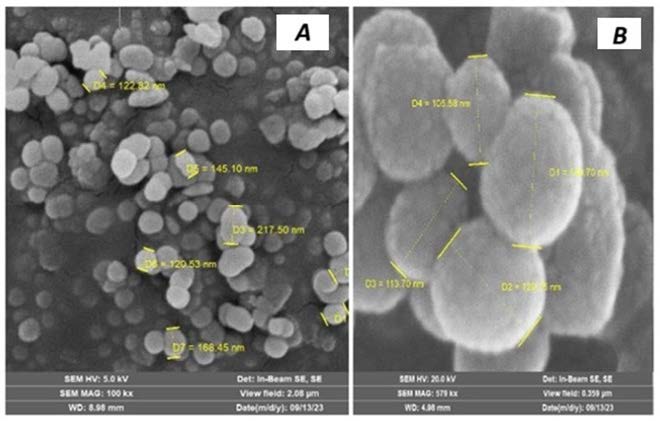
Este articulo evalúa los efectos de curcumina empaquetada en ácido poli(láctico-co-glicólico) (NANO-CUR-PLGA) en el modelo experimental de Enfermedad de Alzheimer inducido Caenorhabditis elegans GMC101. Se realizó la encapsulación de curcumina como principio activo en ácido poli(láctico-co-glicólico) (PLGA) por método químico de emulsión simple y las características fenotípicas de vida útil, movilidad, velocidad máxima y ángulos de movilidad se determinaron a través de videos del modelo invertebrado Caenorhabditis elegans GMC101, cepa mutante que sobre expresa la proteína β-amiloide, las características fueron analizadas por recuentos y las de movilidad por el programa ImageJ utilizando el pluging WrmtracK. Las NANO-CUR-PLGA producidas presentaron un tamaño de 157,4nm ± 7,3 con un promedio de 182,3nm y morfología de esferas individuales, no fusionadas, con una superficie suave. Los cambios fenotípicos de la cepa GMC101, mostraron que la NANO-CUR-PLGA extendió la vida útil de los gusanos hasta el día 14 a la concentración de 1,21µg/ml, mayor tamaño de la cepa GMC101 a la concentración de 0,60 µg/ml, aumento la velocidad máxima y ángulo de movilidad del modelo sin relación a la dosis adicionada de NANO-CUR-PLGA al medio de cultivo.
Descargas
Detalles del artículo
Referencias (VER)
Alam, J.; Dilnawaz, F.; Sahoo, S. K.; Singh, D. V.; Mukhopadhyay, A. K.; Hussain, T.; Pati, S. (2022). Curcumin encapsulated into biocompatible co-polymer PLGA nanoparticle enhanced anti-gastric cancer and anti-Helicobacter pylori effect. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 23(1), 61–70. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2022.23.1.61
Alzheimer’s Association. (2023). 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures (Vol. 19). https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.13016
Bellido-Alocolea, N.; Pérez-Jiménez, M. M.; Muñoz, M. J. (2020). Identification of compounds and genes that affect neurodegenerative diseases in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biosaia, 9.
Busari, Z. A.; Dauda, K. A.; Morenikeji, O. A.; Afolayan, F.; Oyeyemi, O. T.; Meena, J.; Sahu, D.; Panda, A. K. (2017). Antiplasmodial activity and toxicological assessment of curcumin PLGA-encapsulated nanoparticles. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 8, 622. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00622
Cacace, R.; Sleegers, K.; Van Broeckhoven, C. (2016). Molecular genetics of early-onset Alzheimer’s disease revisited. Alzheimer’s & Dementia, 12(6), 733–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2016.01.012
Corsi, A. K.; Wightman, B.; Chalfie, M. (2015). A transparent window into biology: A primer on Caenorhabditis elegans. WormBook: The Online Review of C. elegans Biology, 1–31. https://doi.org/10.1895/wormbook.1.177.1
Coupland, C. A. C.; Hill, T.; Dening, T.; Morriss, R.; Moore, M.; Hippisley-Cox, J. (2019). Anticholinergic drug exposure and the risk of dementia: A nested case-control study. JAMA Internal Medicine, 179(8), 1084–1093. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2019.0677
Cuccioloni, M.; Cecarini, V.; Bonfili, L.; Pettinari, R.; Tombesi, A.; Pagliaricci, N.; Petetta, L.; Angeletti, M.; Eleuteri, A. M. (2022). Enhancing the amyloid-β anti-aggregation properties of curcumin via arene-ruthenium(II) derivatization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(15). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23158710
Danhier, F.; Ansorena, E.; Silva, J. M.; Coco, R.; Le Breton, A.; Préat, V. (2012). PLGA-based nanoparticles: An overview of biomedical applications. Journal of Controlled Release, 161(2), 505–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.01.043
Flibotte, S.; Edgley, M. L.; Chaudhry, I.; Taylor, J.; Neil, S. E.; Rogula, A.; Zapf, R.; Hirst, M.; Butterfield, Y.; Jones, S. J.; Marra, M. A.; Barstead, R. J.; Moerman, D. G. (2010). Whole-genome profiling of mutagenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics, 185(2), 431–441. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.110.116616
Hampel, H.; Mesulam, M. M.; Cuello, A. C.; Farlow, M. R.; Giacobini, E.; Grossberg, G. T.; Khachaturian, A. S.; Vergallo, A.; Cavedo, E.; Snyder, P. J.; Khachaturian, Z. S. (2018). The cholinergic system in the pathophysiology and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain, 141(7), 1917–1933. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awy132
Hampel, H.; Vergallo, A.; Flores Aguilar, L.; Benda, N.; Broich, K.; Cuello, A. C.; Cummings, J.; Dubois, B.; Federoff, H. J.; Fiandaca, M.; Genthon, R.; Haberkamp, M.; Karran, E.; Mapstone, M.; Perry, G.; Schneider, L. S.; Welikovitch, L. A.; Woodcock, J.; Baldacci, F.; Lista, S. (2018). Precision pharmacology for Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacological Research, 130, 331–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2018.02.014
He, W.; Yuan, K.; Ji, B.; Han, Y.; Li, J. (2020). Protective effects of curcumin against neuroinflammation induced by Aβ25-35 in primary rat microglia: Modulation of HMGB1, TLR4 and RAGE expression. Annals of Translational Medicine, 8(4), 88. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.12.147
Jain, R. A. (2000). The manufacturing techniques of various drug loaded biodegradable poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) devices. Biomaterials, 21(23), 2475–2490. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0142-9612(00)00115-0
Kapoor, D. N.; Bhatia, A.; Kaur, R.; Sharma, R.; Kaur, G.; Dhawan, S. (2015). PLGA: A unique polymer for drug delivery. Therapeutic Delivery, 6(1), 41–58. https://doi.org/10.4155/tde.14.91
Khan, S.; Barve, K. H.; Kumar, M. S. (2020). Recent advancements in pathogenesis, diagnostics and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Current Neuropharmacology, 18(11), 1106–1125. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159X18666200528142429
Koopman, M.; Peter, Q.; Seinstra, R. I.; Perni, M.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C. M.; Knowles, T. P. J.; Nollen, E. A. A. (2020). Assessing motor-related phenotypes of Caenorhabditis elegans with the wide field-of-view nematode tracking platform. Nature Protocols, 15(6), 2071–2106. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-020-0321-9
McCall, R. L.; Sirianni, R. W. (2013). PLGA nanoparticles formed by single- or double-emulsion with vitamin E-TPGS. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (82), 51015. https://doi.org/10.3791/51015
National Institutes of Health. (2023). ¿Cómo se trata la enfermedad de Alzheimer? https://www.nia.nih.gov/espanol/cuidado-medico-enfermedad-alzheimer/como-se-trata-enfermedad-alzheimer
Nussbaum-Krammer, C. I.; Neto, M. F.; Brielmann, R. M.; Pedersen, J. S.; Morimoto, R. I. (2015). Investigating the spreading and toxicity of prion-like proteins using the metazoan model organism C. elegans. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (95), 52321. https://doi.org/10.3791/52321
Panda, A. K.; Chakraborty, D.; Sarkar, I.; Khan, T.; Sa, G. (2017). New insights into therapeutic activity and anticancer properties of curcumin. Journal of Experimental Pharmacology, 9, 31–45. https://doi.org/10.2147/JEP.S70568
Reddy, P. H.; Manczak, M.; Yin, X.; Grady, M. C.; Mitchell, A.; Tonk, S.; Kuruva, C. S.; Bhatti, J. S.; Kandimalla, R.; Vijayan, M.; Kumar, S.; Wang, R.; Pradeepkiran, J. A.; Ogunmokun, G.; Thamarai, K.; Quesada, K.; Boles, A.; Reddy, A. P. (2018). Protective effects of Indian spice curcumin against amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 61(3), 843–866. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-170512
Ringman, J. M. (2017). Update on Alzheimer’s and the dementias: Introduction. Neurologic Clinics, 35(2), 171–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2017.01.009
Romero-Vanegas, S. J.; Vargas-González, J. C.; Pardo, R.; Eslava-Schmalbach, J.; Moreno-Angarita, M. (2021). El sistema de salud colombiano y el reconocimiento de la enfermedad de Alzheimer. Revista de Salud Pública, 23(2), e400. https://doi.org/10.15446/rsap.v23n2.88369
Scheltens, P.; De Strooper, B.; Kivipelto, M.; Holstege, H.; Chételat, G.; Teunissen, C. E.; Cummings, J.; van der Flier, W. M. (2021). Alzheimer’s disease. The Lancet, 397(10284), 1577–1590. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32205-4
Stiernagle, T. (2006). Maintenance of C. elegans. WormBook. https://doi.org/10.1895/wormbook.1.101.1
Suárez, H. M.; Díaz Brito. (2020). Eficiencia de encapsulación y capacidad de carga de antocianinas de Vaccinium floribundum Kunt en nanopartículas de zeína. Intelligenza Artificiale, 8, 83–97.
Tagde, P.; Tagde, P.; Islam, F.; Tagde, S.; Shah, M.; Hussain, Z. D.; Rahman, M. H.; Najda, A.; Alanazi, I. S.; Germoush, M. O.; Mohamed, H. R. H.; Algandaby, M. M.; Nasrullah, M. Z.; Kot, N.; Abdel-Daim, M. M. (2021). The multifaceted role of curcumin in advanced nanocurcumin form in the treatment and management of chronic disorders. Molecules, 26(23). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26237109
Tang, C.; Li, L.; Shi, J.; Wu, D.; Wang, M.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, X. (2020). Curcumin in age-related diseases. Die Pharmazie, 75(11), 534–539. https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2020.0760
Teymouri, M.; Pirro, M.; Johnston, T. P.; Sahebkar, A. (2017). Curcumin as a multifaceted compound against human papilloma virus infection and cervical cancers: A review of chemistry, cellular, molecular, and preclinical features. BioFactors, 43(3), 331–346. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1344
Waghela, B. N.; Sharma, A.; Dhumale, S.; Pandey, S. M.; Pathak, C. (2015). Curcumin conjugated with PLGA potentiates sustainability, anti-proliferative activity and apoptosis in human colon carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE, 10(2), e0117526. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0117526
Xu, J.; Du, P.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, C. (2023). Curcumin supplementation increases longevity and antioxidant capacity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 14, 1195490. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2023.1195490
Yang, H.; Zeng, F.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, C.; Ran, C.; Yang, J. (2022). Curcumin scaffold as a multifunctional tool for Alzheimer’s disease research. Molecules, 27(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27123879
Zendehdel, E.; Abdollahi, E.; Momtazi-Borojeni, A. A.; Korani, M.; Alavizadeh, S. H.; Sahebkar, A. (2019). The molecular mechanisms of curcumin’s inhibitory effects on cancer stem cells. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 120(4), 4739–4757. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27757
Zhang, S.; Li, F.; Zhou, T.; Wang, G.; Li, Z. (2020). Caenorhabditis elegans as a useful model for studying aging mutations. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00637
Zhang, X. X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z. T.; Ma, Y. H.; Tan, L.; Yu, J. T. (2021). The epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease: Modifiable risk factors and prevention. The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease, 8(3), 313–321. https://doi.org/10.14283/jpad.2021.15
Zhen, M.; Samuel, A. D. T. (2015). C. elegans locomotion: Small circuits, complex functions. Current Opinion in Neurobiology, 33, 117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conb.2015.03.009
Zhou, Z.; Sun, T.; Jiang, C. (2021). Recent advances on drug delivery nanocarriers for cerebral disorders. Biomedical Materials, 16(2), 24104. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-605X/abdc97

 PDF
PDF
 FLIP
FLIP